Novox Caplets
This page contains information on Novox Caplets for veterinary use.The information provided typically includes the following:
- Novox Caplets Indications
- Warnings and cautions for Novox Caplets
- Direction and dosage information for Novox Caplets
Novox Caplets
This treatment applies to the following species: Company: Vedco
Company: Vedco
(carprofen)
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug
For oral use in dogs only
Novox Caplets Caution
Federal law restricts this drug to use by or on the order of a licensed veterinarian.
Description
Carprofen is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) of the propionic acid class that includes ibuprofen, naproxen, and ketoprofen. Carprofen is the nonproprietary designation for a substituted carbazole, 6-chloro-α-methyl-9H-carbazole-2-acetic acid. The empirical formula is C15H12ClNO2 and the molecular weight 273.72. The chemical structure of carprofen is:
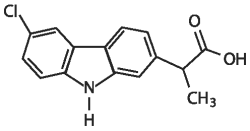
Carprofen is a white, crystalline compound. It is freely soluble in ethanol, but practically insoluble in water at 25°C.
Clinical Pharmacology
Carprofen is a non-narcotic, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory agent with characteristic analgesic and antipyretic activity approximately equipotent to indomethacin in animal models.1The mechanism of action of carprofen, like that of other NSAIDs, is believed to be associated with the inhibition of cyclooxygenase activity. Two unique cyclooxygenases have been described in mammals.2 The constitutive cyclooxygenase, COX-1, synthesizes prostaglandins necessary for normal gastrointestinal and renal function. The inducible cyclooxygenase, COX-2, generates prostaglandins involved in inflammation. Inhibition of COX-1 is thought to be associated with gastrointestinal and renal toxicity while inhibition of COX-2 provides anti-inflammatory activity. The specificity of a particular NSAID for COX-2 versus COX-1 may vary from species to species.3 In an in vitro study using canine cell cultures, carprofen demonstrated selective inhibition of COX-2 versus COX-1.4 Clinical relevance of these data has not been shown. Carprofen has also been shown to inhibit the release of several prostaglandins in two inflammatory cell systems: rat polymorphonuclear leukocytes (PMN) and human rheumatoid synovial cells, indicating inhibition of acute (PMN system) and chronic (synovial cell system) inflammatory reactions.1
Several studies have demonstrated that carprofen has modulatory effects on both humoral and cellular immune responses.5-9 Data also indicate that carprofen inhibits the production of osteoclast-activating factor (OAF), PGE1, and PGE2 by its inhibitory effects on prostaglandin biosynthesis.1
Based upon comparison with data obtained from intravenous administration, carprofen is rapidly and nearly completely absorbed (more than 90% bioavailable) when administered orally.10 Peak blood plasma concentrations are achieved in 1-3 hours after oral administration of 1, 5, and 25 mg/kg to dogs. The mean terminal half-life of carprofen is approximately 8 hours (range 4.5-9.8 hours) after single oral doses varying from 1-35 mg/kg of body weight. After a 100 mg single intravenous bolus dose, the mean elimination half-life was approximately 11.7 hours in the dog. Carprofen is more than 99% bound to plasma protein and exhibits a very small volume of distribution.
Carprofen is eliminated in the dog primarily by biotransformation in the liver followed by rapid excretion of the resulting metabolites (the ester glucuronide of carprofen and the ether glucuronides of 2 phenolic metabolites, 7-hydroxy-carprofen and 8-hydroxy carprofen) in the feces (70-80%) and urine (10-20%). Some enterohepatic circulation of the drug is observed.
Novox Caplets Indications
Carprofen is indicated for the relief of pain and inflammation associated with osteoarthritis and for the control of postoperative pain associated with soft tissue and orthopedic surgeries in dogs.
Contraindications
Carprofen should not be used in dogs exhibiting previous hypersensitivity to carprofen.
Precautions
As a class, cyclooxygenase inhibitory NSAIDs may be associated with gastrointestinal, renal and hepatic toxicity. Effects may result from decreased prostaglandin production and inhibition of the enzyme cyclooxygenase which is responsible for the formation of prostaglandins from arachidonic acid.11-14 When NSAIDs inhibit prostaglandins that cause inflammation they may also inhibit those prostaglandins which maintain normal homeostatic function. These anti-prostaglandin effects may result in clinically significant disease in patients with underlying or pre-existing disease more often than in healthy patients.12,14 NSAID therapy could unmask occult disease which has previously been undiagnosed due to the absence of apparent clinical signs. Patients with underlying renal disease for example, may experience exacerbation or decompensation of their renal disease while on NSAID therapy.11-14 The use of parenteral fluids during surgery should be considered to reduce the potential risk of renal complications when using NSAIDs perioperatively.Carprofen is an NSAID, and as with others in that class, adverse reactions may occur with its use. The most frequently reported effects have been gastrointestinal signs. Events involving suspected renal, hematologic, neurologic, dermatologic, and hepatic effects have also been reported. Patients at greatest risk for renal toxicity are those that are dehydrated, on concomitant diuretic therapy, or those with renal, cardiovascular, and/or hepatic dysfunction. Concurrent administration of potentially nephrotoxic drugs should be approached cautiously, with appropriate monitoring. Since NSAIDs possess the potential to induce gastrointestinal ulcerations and/or gastrointestinal perforations, concomitant use of carprofen and other anti-inflammatory drugs, such as NSAIDs or corticosteroids, should be avoided. If additional pain medication is needed after administration of the total daily dose of carprofen, a non-NSAID or non-corticosteroid class of analgesia should be considered. The use of another NSAID is not recommended. Sensitivity to drug-associated adverse reactions varies with the individual patient. Carprofen treatment was not associated with renal toxicity or gastrointestinal ulceration in well-controlled safety studies of up to ten times the dose in dogs.
Novox® Caplets is not recommended for use in dogs with bleeding disorders (e.g., Von Willebrand’s disease), as safety has not been established in dogs with these disorders. The safe use of Novox® Caplets in animals less than 6 weeks of age, pregnant dogs, dogs used for breeding purposes, or in lactating bitches has not been established. Studies to determine the activity of carprofen when administered concomitantly with other protein-bound or similarly metabolized drugs have not been conducted.
Drug compatibility should be monitored closely in patients requiring additional therapy. Such drugs commonly used include cardiac, anticonvulsant and behavioral medications. It has been suggested that treatment with carprofen may reduce the level of inhalant anesthetics needed.15
If additional pain medication is warranted after administration of the total daily dose of Novox® Caplets, alternative analgesia should be considered. The use of another NSAID is not recommended. Consider appropriate washout times when switching from one NSAID to another or when switching from corticosteroid use to NSAID use.
Warnings
Keep out of reach of children. Not for human use.
Consult a physician in cases of accidental ingestion by humans. For use in dogs only. Do not use in cats.
All dogs should undergo a thorough history and physical examination before initiation of NSAID therapy. Appropriate laboratory tests to establish hematological and serum biochemical baseline data prior to, and periodically during, administration of any NSAID should be considered. Owners should be advised to observe for signs of potential drug toxicity (see Information for Dog Owners, Adverse Reactions, Animal Safety and Post-Approval Experience).
INFORMATION FOR DOG OWNERS:
Novox® Caplets, like other drugs of its class, is not free from adverse reactions. Owners should be advised of the potential for adverse reactions and be informed of the clinical signs associated with drug intolerance. Adverse reactions may include decreased appetite, vomiting, diarrhea, dark or tarry stools, increased water consumption, increased urination, pale gums due to anemia, yellowing of gums, skin or white of the eye due to jaundice, lethargy, incoordination, seizure, or behavioral changes.
Serious adverse reactions associated with this drug class can occur without warning and in rare situations result in death (see Adverse Reactions). Owners should be advised to discontinue Novox® Caplets therapy and contact their veterinarian immediately if signs of intolerance are observed.
The vast majority of patients with drug related adverse reactions have recovered when the signs are recognized, the drug is withdrawn and veterinary care, if appropriate, is initiated. Owners should be advised of the importance of periodic follow up for all dogs during administration of any NSAID.
Adverse Reactions
During investigational studies of osteoarthritis with twice daily administration of 1 mg/lb, no clinically significant adverse reactions were reported. Some clinical signs were observed during field studies (n=297) which were similar for carprofen caplet- and placebo-treated dogs. Incidences of the following were observed in both groups: vomiting (4%), diarrhea (4%), changes in appetite (3%), lethargy (1.4%), behavioral changes (1%), and constipation (0.3%). The product vehicle served as control.
There were no serious adverse events reported during clinical field studies with once daily oral administration of 2 mg/lb. The following categories of abnormal health observations were reported. The product vehicle served as control.
Percentage of Dogs with Abnormal Health Observations Reported in Clinical Field Study (2 mg/lb once daily)
|
Observation |
carprofen (n=129) |
Placebo (n=132) |
|
Inappetence |
1.6 |
1.5 |
|
Vomiting |
3.1 |
3.8 |
|
Diarrhea/Soft stool |
3.1 |
4.5 |
|
Behavior change |
0.8 |
0.8 |
|
Dermatitis |
0.8 |
0.8 |
|
PU/PD |
0.8 |
-- |
|
SAP increase |
7.8 |
8.3 |
|
ALT increase |
5.4 |
4.5 |
|
AST increase |
2.3 |
0.8 |
|
BUN increase |
3.1 |
1.5 |
|
Bilirubinuria |
16.3 |
12.1 |
|
Ketonuria |
14.7 |
9.1 |
Clinical pathology parameters listed represent reports of increases from pre-treatment values; medical judgment is necessary to determine clinical relevance.
During investigational studies of surgical pain for the caplet formulation, no clinically significant adverse reactions were reported. The product vehicle served as control.
Percentage of Dogs with Abnormal Health Observations Reported in Surgical Pain Field Studies with Caplets (2 mg/lb once daily)
|
Observation* |
carprofen (n=148) |
Placebo (n=149) |
|
Vomiting |
10.1 |
13.4 |
|
Diarrhea/Soft stool |
6.1 |
6.0 |
|
Ocular disease |
2.7 |
0 |
|
Inappetence |
1.4 |
0 |
|
Dermatitis/skin lesion |
2.0 |
1.3 |
|
Dysrhythmia |
0.7 |
0 |
|
Apnea |
1.4 |
0 |
|
Oral/periodontal disease |
1.4 |
0 |
|
Pyrexia |
0.7 |
1.3 |
|
Urinary tract disease |
1.4 |
1.3 |
|
Wound drainage |
1.4 |
0 |
*A single dog may have experienced more than one occurrence of an event.
Post-Approval Experience:
Although not all adverse reactions are reported, the following adverse reactions are based on voluntary post-approval adverse drug experience reporting. The categories of adverse reactions are listed in decreasing order of frequency by body system.
Gastrointestinal: Vomiting, diarrhea, constipation, inappetence, melena, hematemesis, gastrointestinal ulceration, gastrointestinal bleeding, pancreatitis.
Hepatic: Inappetence, vomiting, jaundice, acute hepatic toxicity, hepatic enzyme elevation, abnormal liver function test(s), hyperbilirubinemia, bilirubinuria, hypoalbuminemia. Approximately one-fourth of hepatic reports were in Labrador Retrievers.
Neurologic: Ataxia, paresis, paralysis, seizures, vestibular signs, disorientation.
Urinary: Hematuria, polyuria, polydipsia, urinary incontinence, urinary tract infection, azotemia, acute renal failure, tubular abnormalities including acute tubular necrosis, renal tubular acidosis, glucosuria.
Behavioral: Sedation, lethargy, hyperactivity, restlessness, aggressiveness.
Hematologic: Immune-mediated hemolytic anemia, immune-mediated thrombocytopenia, blood loss anemia, epistaxis.
Dermatologic: Pruritus, increased shedding, alopecia, pyotraumatic moist dermatitis (hot spots), necrotizing panniculitis/vasculitis, ventral ecchymosis.
Immunologic or hypersensitivity: Facial swelling, hives, erythema.
In rare situations, death has been associated with some of the adverse reactions listed above.
To report a suspected adverse reaction call 1-888-708-3326.
Dosage and Administration
Always provide Client Information Sheet with prescription. Carefully consider the potential benefits and risk of Carprofen and other treatment options before deciding to use Carprofen. Use the lowest effective dose for the shortest duration consistent with individual response. The recommended dosage for oral administration to dogs is 2 mg/lb (4.4 mg/kg) of body weight daily. The total daily dose may be administered as 2 mg/lb of body weight once daily or divided and administered as 1 mg/lb (2.2 mg/kg) twice daily. For the control of postoperative pain, administer approximately 2 hours before the procedure. Caplets are scored and dosage should be calculated in half-caplet increments.Effectiveness
Confirmation of the effectiveness of carprofen for the relief of pain and inflammation associated with osteoarthritis and for the control of postoperative pain associated with soft tissue and orthopedic surgeries, was demonstrated in 5 placebo-controlled, masked studies examining the anti-inflammatory and analgesic effectiveness of carprofen in various breeds of dogs.Separate placebo-controlled, masked, multicenter field studies confirmed the anti-inflammatory and analgesic effectiveness of carprofen when dosed at 2 mg/lb once daily or when divided and administered at 1 mg/lb twice daily. In these two field studies, dogs diagnosed with osteoarthritis showed statistically significant overall improvement based on lameness evaluations by the veterinarian and owner observations when administered carprofen at labeled doses.
Separate placebo-controlled, masked, multicenter field studies confirmed the effectiveness of carprofen for the control of postoperative pain when, dosed at 2 mg/lb once daily in various breeds of dogs. In these studies, dogs presented for ovariohysterectomy, cruciate repair and aural surgeries were administered carprofen preoperatively and for a maximum of 3 days (soft tissue) or 4 days (orthopedic) postoperatively. In general, dogs administered carprofen showed statistically significant improvement in pain scores compared to controls.
ANIMAL SAFETY STUDIES: Laboratory studies in unanesthetized dogs and clinical field studies have demonstrated that carprofen is well tolerated in dogs after oral administration.
In target animal safety studies, carprofen was administered orally to healthy Beagle dogs at 1, 3, and 5 mg/lb twice daily (1, 3 and 5 times the recommended total daily dose) for 42 consecutive days with no significant adverse reactions. Serum albumin for a single female dog receiving 5 mg/lb twice daily decreased to 2.1 g/dL after 2 weeks of treatment, returned to the pre-treatment value (2.6 g/dL) after 4 weeks of treatment, and was 2.3 g/dL at the final 6-week evaluation. Over the 6-week treatment period, black or bloody stools were observed in 1 dog (1 incident) treated with 1 mg/lb twice daily and in 1 dog (2 incidents) treated with 3 mg/lb twice daily. Redness of the colonic mucosa was observed in 1 male that received 3 mg/lb twice daily.
Two of 8 dogs receiving 10 mg/lb orally twice daily (10 times the recommended total daily dose) for 14 days exhibited hypoalbuminemia. The mean albumin level in the dogs receiving this dose was lower (2.38 g/dL) than each of 2 placebo control groups (2.88 and 2.93 g/dL, respectively). Three incidents of black or bloody stool were observed in 1 dog. Five of 8 dogs exhibited reddened areas of duodenal mucosa on gross pathologic examination. Histologic examination of these areas revealed no evidence of ulceration, but did show minimal congestion of the lamina propria in 2 of the 5 dogs.
In separate safety studies lasting 13 and 52 weeks, respectively, dogs were administered orally up to 11.4 mg/lb/day (5.7 times the recommended total daily dose of 2 mg/lb) of carprofen. In both studies, the drug was well tolerated clinically by all of the animals. No gross or histologic changes were seen in any of the treated animals. In both studies, dogs receiving the highest doses had average increases in serum L-alanine aminotransferase (ALT) of approximately 20 IU.
In the 52-week study, minor dermatologic changes occurred in dogs in each of the treatment groups but not in the control dogs. The changes were described as slight redness or rash and were diagnosed as non-specific dermatitis. The possibility exists that these mild lesions were treatment related, but no dose relationship was observed.
Clinical field studies were conducted with 549 dogs of different breeds at the recommended oral doses for 14 days (297 dogs were included in a study evaluating 1 mg/lb twice daily and 252 dogs were included in a separate study evaluating 2 mg/lb once daily). In both studies the drug was clinically well tolerated and the incidence of clinical adverse reactions for carprofen-treated animals was no higher than placebo-treated animals (placebo contained inactive ingredients found in carprofen caplets). For animals receiving 1 mg/lb twice daily, the mean post-treatment serum ALT values were 11 IU greater and 9 IU less than pre-treatment values for dogs receiving carprofen and placebo, respectively. Differences were not statistically significant. For animals receiving 2 mg/lb once daily, the mean post-treatment serum ALT values were 4.5 IU greater and 0.9 IU less than pre-treatment values for dogs receiving carprofen and placebo, respectively. In the latter study, 3 carprofen-treated dogs developed a 3-fold or greater increase in (ALT) and/or (AST) during the course of therapy. One placebo-treated dog had a greater than 2-fold increase in ALT. None of these animals showed clinical signs associated with the laboratory value changes. Changes in clinical laboratory values (hematology and clinical chemistry) were not considered clinically significant. The 1 mg/lb twice daily course of therapy was repeated as needed at 2-week intervals in 244 dogs, some for as long as 5 years.
Clinical field studies were conducted in 297 dogs of different breeds undergoing orthopedic or soft tissue surgery. Dogs were administered 2 mg/lb of carprofen caplets two hours prior to surgery then once daily, as needed for 2 days (soft tissue surgery) or 3 days (orthopedic surgery). Carprofen was well tolerated when used in conjunction with a variety of anesthetic-related drugs. The type and severity of abnormal health observations in carprofen- and placebo-treated animals were approximately equal and few in number (see Adverse Reactions). The most frequent abnormal health observation was vomiting and was observed at approximately the same frequency in carprofen- and placebo-treated animals. Changes in clinicopathologic indices of hematopoietic, renal, hepatic, and clotting function were not clinically significant. The mean post-treatment serum ALT values were 7.3 IU and 2.5 IU less than pre-treatment values for dogs receiving carprofen and placebo, respectively. The mean post-treatment AST values were 3.1 IU less for dogs receiving carprofen and 0.2 IU greater for dogs receiving placebo.
Storage
Store at controlled room temperature 15°-30°C (59° - 86°F).
How Supplied
Novox® Caplets are scored, and contain 25 mg, 75 mg, or 100 mg of carprofen per caplet. Each caplet size is packaged in bottles containing 30, 60, or 180 caplets.
|
|
|
NDC |
|
|
25 MG |
30 CAPLETS |
50989-236-02 |
001702L01 |
|
60 CAPLETS |
50989-236-50 |
002762L01 |
|
|
180 CAPLETS |
50989-236-86 |
024670L01 |
|
|
75 MG |
30 CAPLETS |
50989-238-02 |
004762L01 |
|
60 CAPLETS |
50989-238-50 |
005762L01 |
|
|
180 CAPLETS |
50989-238-86 |
006762L01 |
|
|
100 MG |
30 CAPLETS |
50989-245-02 |
007762L01 |
|
60 CAPLETS |
50989-245-50 |
008762L01 |
|
|
180 CAPLETS |
50989-245-86 |
009762L01 |
References
1. Baruth H, et al: In Anti-Inflammatory and Anti-Rheumatic Drugs, Vol. II, Newer Anti-Inflammatory Drugs, Rainsford KD, ed. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp. 33-47, 1986.
2. Vane JR, Botting RM: Mechanism of action of anti-inflammatory drugs. Scand J Rheumatol 25:102, pp. 9-21.
3. Grossman CJ, Wiseman J, Lucas FS, et al: Inhibition of constitutive and inducible cyclooxygenase activity in human platelets and mononuclear cells by NSAIDs and COX-2 inhibitors. Inflammation Research 44:253-257, 1995.
4. Ricketts AP, Lundy KM, Seibel SB: Evaluation of selective inhibition of canine cyclooxygenase 1 and 2 by carprofen and other nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Am J Vet Res 59:11, pp. 1441-1446, November 1998.
5. Ceuppens JL, et al: Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory agents inhibit the synthesis of IgM rheumatoid factor in vitro. Lancet 1:528, 1982.
6. Ceuppens JL, et al: Endogenous prostaglandin E2 enhances polyclonal immunoglobulin production by ionically inhibiting T suppressor cell activity. Cell Immunol 70:41, 1982.
7. Schleimer RP, et al: The effects of prostaglandin synthesis inhibition on the immune response. Immunopharmacology 3:205, 1981.
8. Leung KH, et al: Modulation of the development of cell mediated immunity: possible roles of the products of cyclooxygenase and lipoxygenase pathways of arachidonic acid metabolism. Int J Immunopharmacology 4:195, 1982.
9. Veit BC: Immunoregulatory activity of cultured-induced suppressor macrophages. Cell Immunol 72:14, 1982.
10. Schmitt M, et al: Biopharmaceutical evaluation of carprofen following single intravenous, oral, and rectal doses in dogs. Biopharm Drug Dispos 11(7):585-94, 1990.
11. Kore AM: Toxicology of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Veterinary Clinics of North America, Small Animal Practice 20, March 1990.
12. Binns SH: Pathogenesis and pathophysiology of ischemic injury in cases of acute renal failure. Compend for Cont Ed 16:1, January 1994.
13. Boothe DM: Prostaglandins: Physiology and clinical implications. Compend for Cont Ed 6:11, November 1984.
14. Rubin SI: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, prostaglandins, and the kidney. JAVMA 188:9, May 1986.
15. Ko CH, Lange DN, Mandsager RE, et al: Effects of butorphanol and carprofen on the minimal alveolar concentration of isoflurane in dogs. JAVMA 217:1025-1028, 2000.
For a copy of the Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) or to report adverse reactions call Vedco, Inc. at 1-888-708-3326.
ANADA 200-498, Approved by FDA
Manufactured By: Norbrook Laboratories Limited, Newry, Northern Ireland
Distributed By: Vedco, Inc., St. Joseph, MO 64507
®Novox is a registered trademark of Vedco, Inc.
001762I01
CPN: 1094273.3
5503 CORPORATE DR., ST. JOSEPH, MO, 64507
| Telephone: | 816-238-8840 | |
| Toll-Free: | 888-708-3326 (888-70VEDCO) | |
| Fax: | 816-238-1837 | |
| Website: | www.vedco.com |
 |
THIS SERVICE AND DATA ARE PROVIDED "AS IS". DVMetrics assumes no liability, and each user assumes full risk, responsibility, and liability, related to its use of the DVMetrics service and data. See the Terms of Use for further details. |
Copyright © 2024 Animalytix LLC. Updated: 2024-02-27
